L-Theanine and Seizures: Exploring the Potential Risks and Benefits
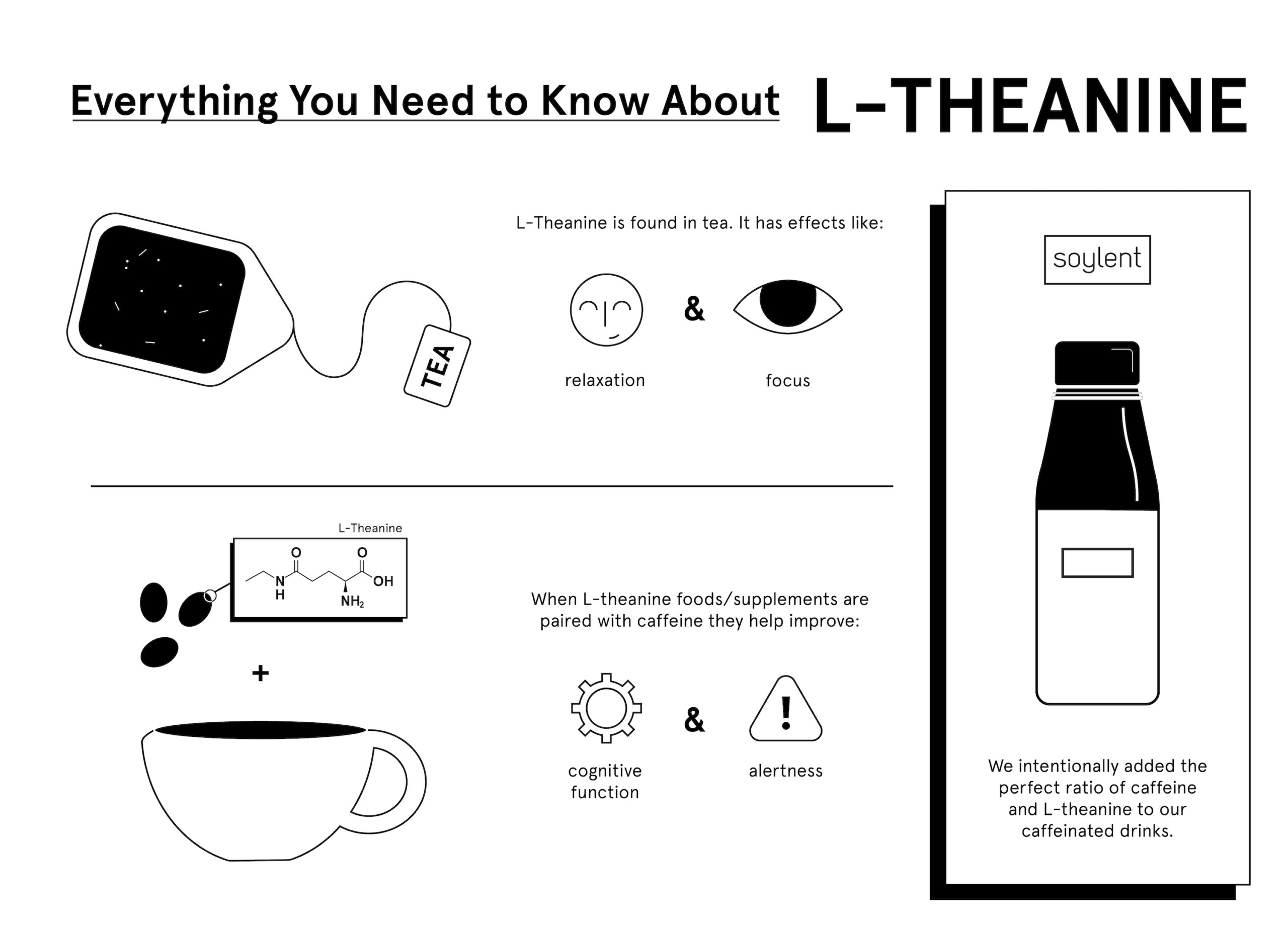
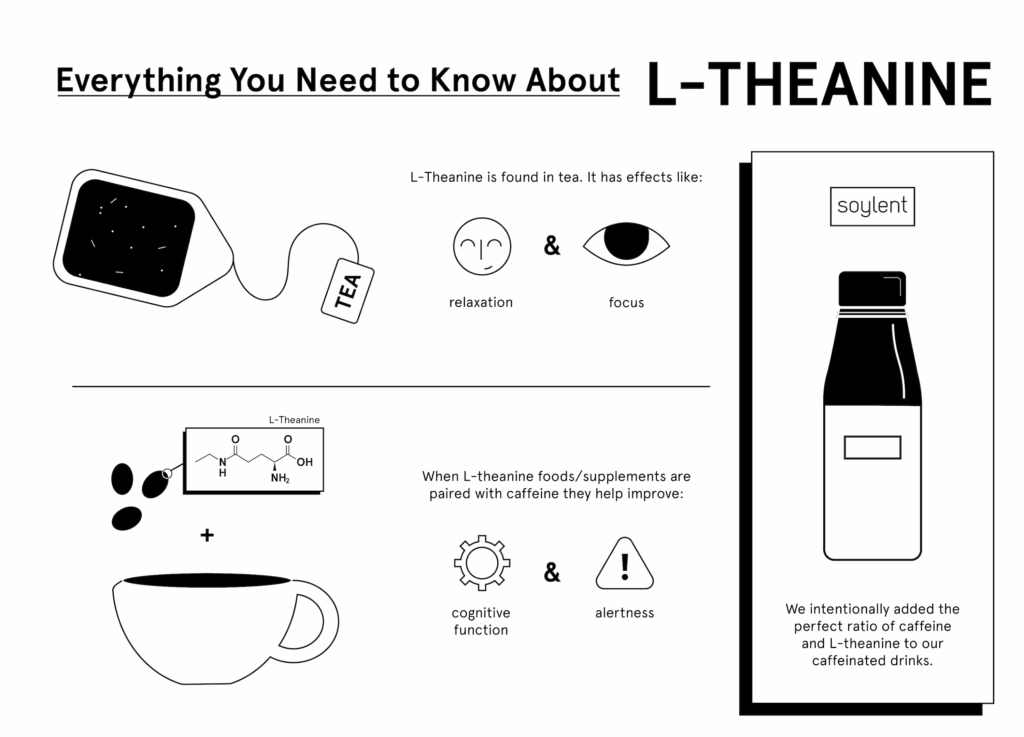
L-theanine, an amino acid primarily found in green tea leaves, has gained considerable attention for its potential calming and cognitive-enhancing properties. Marketed as a natural supplement to reduce stress and anxiety, and improve focus, it’s crucial to understand its possible interactions, especially concerning neurological conditions. This article delves into the relationship between l-theanine and seizures, examining available research, potential risks, and benefits, and offering a balanced perspective for individuals considering its use.
Understanding L-Theanine
L-theanine is a non-protein amino acid that is structurally similar to glutamate, a neurotransmitter involved in brain function. It is known to cross the blood-brain barrier, where it can influence neurotransmitter levels. Research suggests that l-theanine may increase levels of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety. It also modulates dopamine and serotonin levels, further contributing to its mood-enhancing effects. These properties have led to its popularity as a natural anxiolytic and cognitive enhancer.
The Connection Between L-Theanine and Seizures: What Does the Research Say?
The scientific literature on the direct effects of l-theanine on seizures is limited and somewhat conflicting. Some studies suggest that l-theanine may have anticonvulsant properties, while others raise concerns about potential proconvulsant effects in certain individuals. It’s vital to emphasize that much of the research is preclinical, involving animal models, and human studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions.
Potential Anticonvulsant Effects
Some research indicates that l-theanine might possess anticonvulsant properties. This is primarily attributed to its ability to modulate excitatory neurotransmitters, potentially reducing neuronal excitability. A study published in the journal *Epilepsy Research* explored the effects of l-theanine on chemically induced seizures in mice. The results suggested that l-theanine administration led to a reduction in seizure severity and duration. However, it’s important to note that these findings are preliminary and require confirmation in human trials.
Potential Proconvulsant Effects and Considerations
Conversely, there are concerns that l-theanine could potentially trigger or worsen seizures in some individuals. This is based on the understanding that l-theanine can influence glutamate levels, and excessive glutamate activity is known to contribute to seizure generation. While l-theanine generally promotes relaxation, in certain circumstances, it could potentially disrupt the delicate balance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter activity in the brain, leading to a proconvulsant effect. Individuals with pre-existing seizure disorders or those taking medications that affect neurotransmitter activity should exercise caution. [See also: Interactions Between L-Theanine and Anti-Seizure Medications]
Factors Influencing the Risk of Seizures with L-Theanine
Several factors can influence the potential risk of seizures associated with l-theanine supplementation:
- Dosage: Higher doses of l-theanine may increase the likelihood of adverse effects, including potential proconvulsant activity.
- Individual Sensitivity: Individuals with pre-existing neurological conditions, such as epilepsy or a history of seizures, may be more susceptible to the effects of l-theanine on brain excitability.
- Medications: L-theanine may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect neurotransmitter activity, such as antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and anti-seizure medications.
- Underlying Health Conditions: People with certain health conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, may process l-theanine differently, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects.
Who Should Exercise Caution?
Given the limited research and potential risks, certain individuals should exercise caution when considering l-theanine supplementation:
- Individuals with Epilepsy or a History of Seizures: Due to the potential for l-theanine to alter neurotransmitter activity, individuals with epilepsy or a history of seizures should consult with their doctor before taking l-theanine.
- Individuals Taking Anti-Seizure Medications: L-theanine could potentially interact with anti-seizure medications, altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: There is limited research on the safety of l-theanine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is generally recommended to avoid its use during these times.
- Individuals with Liver or Kidney Disease: People with liver or kidney disease may process l-theanine differently, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects.
Potential Benefits of L-Theanine
While the primary focus is on the potential risks related to seizures, it’s important to acknowledge the potential benefits of l-theanine, which have contributed to its widespread use as a supplement:
- Reduced Anxiety and Stress: L-theanine has been shown to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety by increasing levels of GABA and modulating other neurotransmitters.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that l-theanine may enhance cognitive function, including attention, focus, and memory.
- Enhanced Sleep Quality: L-theanine may promote relaxation and improve sleep quality by reducing anxiety and promoting a sense of calm.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Research suggests that l-theanine may have neuroprotective effects, protecting brain cells from damage.
Recommendations and Precautions
If you are considering taking l-theanine, it is essential to follow these recommendations:
- Consult with Your Doctor: Before taking l-theanine, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications, consult with your doctor to discuss the potential risks and benefits.
- Start with a Low Dose: Begin with a low dose of l-theanine and gradually increase it as tolerated.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Pay attention to any side effects you experience while taking l-theanine, and discontinue use if you experience any adverse reactions.
- Purchase from Reputable Sources: Buy l-theanine supplements from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and purity.
Conclusion
The relationship between l-theanine and seizures is complex and requires further research. While some studies suggest potential anticonvulsant properties, there are also concerns about potential proconvulsant effects in certain individuals. Individuals with epilepsy or a history of seizures, those taking anti-seizure medications, and pregnant or breastfeeding women should exercise caution and consult with their doctor before taking l-theanine. A balanced approach that considers both the potential risks and benefits is crucial for making informed decisions about l-theanine supplementation.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.